CRYSTALLINE SILICA DUST EXPOSURE
Is silica dust dangerous? Absolutely. Crystalline silica dust poses a considerable risk to health in specific work environments. It’s a carcinogenic and mutagenic substance known to cause severe respiratory problems like silicosis and other lung diseases. For this reason, ensuring safe working conditions for individuals exposed to silica dust is mandatory.
Implementing effective preventive measures is essential to minimize these hazards, and all regulations recognize them as:
Numerous work activities release crystalline silica dust, spanning various sectors:

In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) was the first to regulate the maximum possible exposure to silica dust and issued specific standards for the management of crystalline silica dust.
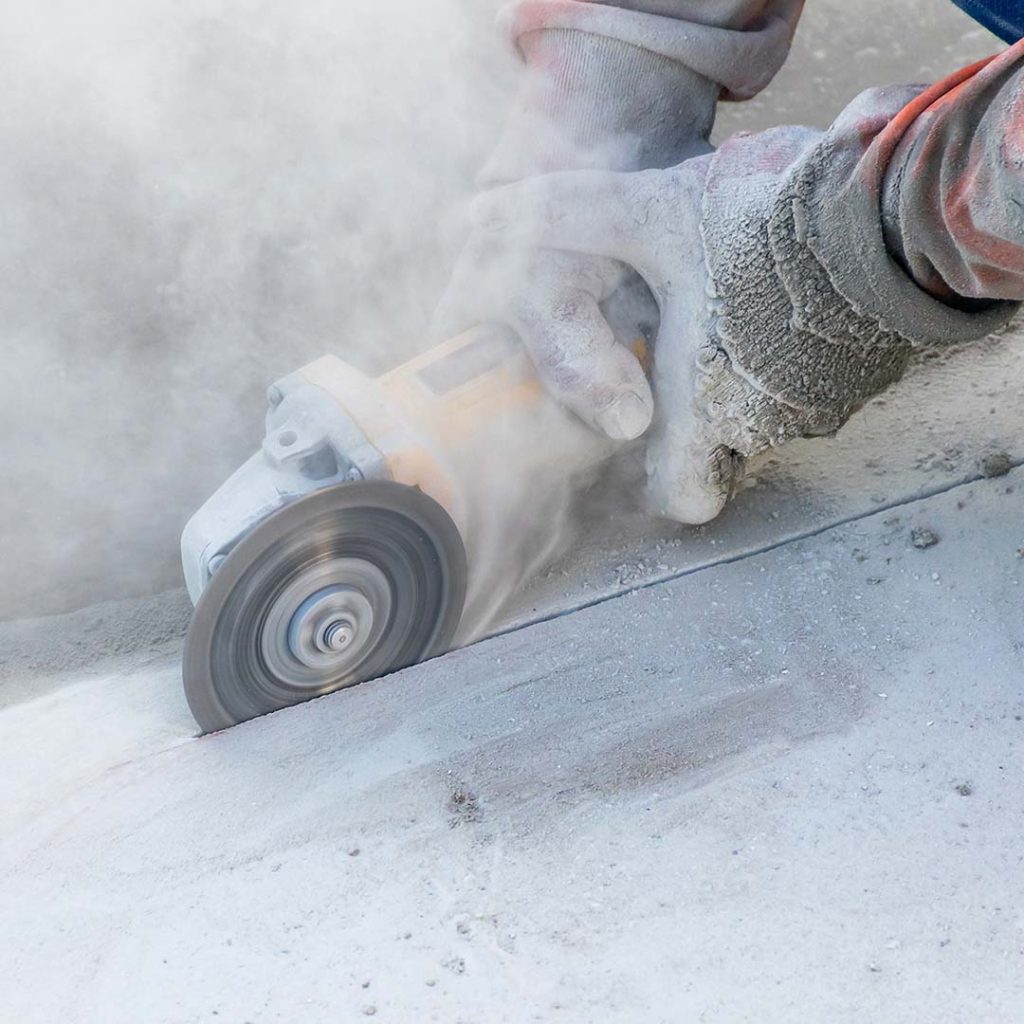
It is mandatory to take control of employees’ dust exposure by following OSHA’s recommended methods for removing silica dust particulates. Utilize proper industrial vacuums to minimize hazards during material breakage and implement engineering control measures to extract, ventilate, and eliminate silica dust near production areas will protect workers’ health and let your company be compliant to regulations.
The landmark regulation for respirable crystalline silica dust is OSHA regulation 29 CFR 1926.1153, which establishes the following requirements for employers:
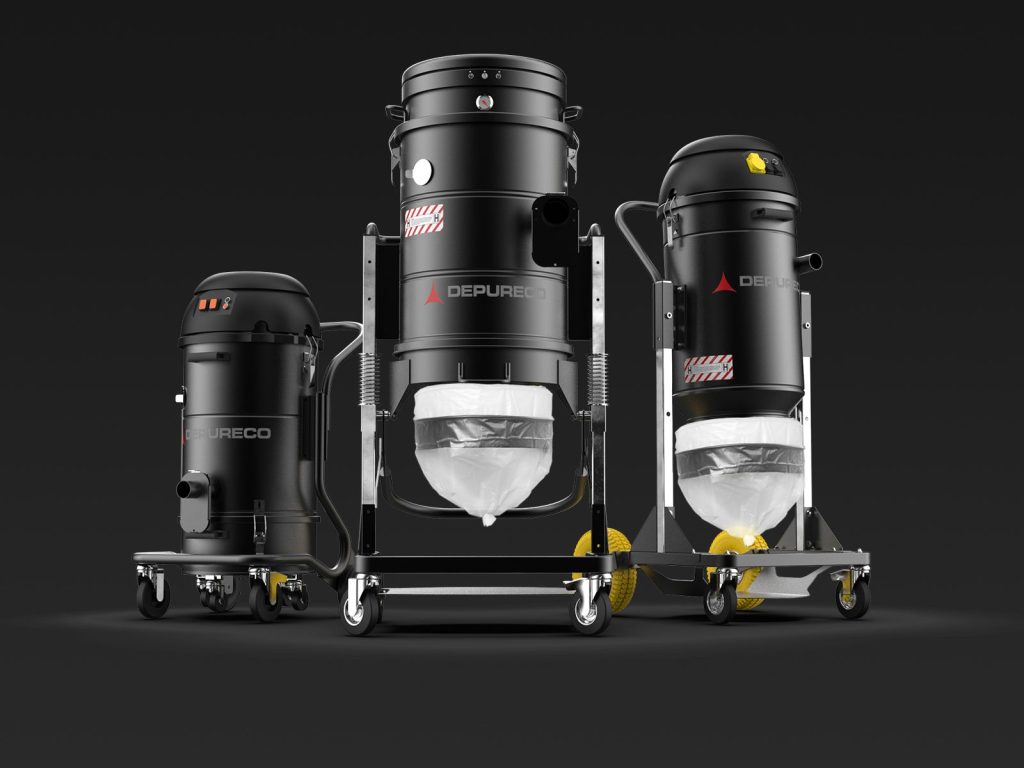


Regulations recognize the use of HEPA dust extractors as a top-notch solution for mitigating risks associated with silica dust. These extractors must have specific features to ensure their suitability for silica dust applications:
How to protect your workers from silica dust, according to OSHA regulations? By filtering with the maximum efficiency the fine silica dust that generates when cutting, grinding, drilling or sanding materials such as concrete, brick, stone, and tiles.
H14 filters are designed to remove a high percentage of airborne particles, including those as small as 0.18 micrometers, with an efficiency of at least 99.995%.

We will give you all the required information